It is with great sadness and heavy heart that we announce the recent passing of Dr. Mikhail (Misha) V. Blagosklonny, our beloved Editor-in-Chief. Misha succumbed to metastatic lung cancer after a courageous battle.
Dr. Blagosklonny will be remembered as a brilliant and extraordinary scientist who dedicated his life to science. He was a visionary thinker, who made highly original contributions to cancer and aging research that were often ahead of their time.
Dr. Blagosklonny was born into a family of scientists. His mother, Professor of Medicine Yanina V. Blagosklonnaya, specialized in endocrinology and was a talented teacher, mentoring several generations of medical students. His father, Professor Vladimir M. Dilman, was a brilliant gerontologist, endocrinologist and oncologist, known for being a very charismatic person. He was the first person to encourage Misha to think about nature, aging, and philosophy.
Misha was a theorist by nature. While in school, he was deeply interested in physics and dreamed of becoming a theoretical physicist. Eventually, he chose biology, driven to study aging and age-related diseases, including cancer. He started as an experimentalist, but over the years, he became a theoretical biologist. In a way, his dream came true.
After earning his MD/PhD in cardiology and experimental medicine from Pavlov First State Medical University of St. Petersburg, Dr. Blagosklonny was awarded a prestigious Fogarty Fellowship from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in Bethesda, MD. During his productive fellowship at the National Cancer Institute (NCI) in Dr. Leonard M. Neckers’s laboratory, he co-authored 18 publications in diverse areas of cancer research and was the last author on a clinical phase I/II trial paper. Then, he held a brief but productive senior research fellowship at the University of Pennsylvania in Dr. Wafik S El-Deiry’s laboratory before returning for several years to the NCI, where he collaborated with Dr. Tito Fojo. During those years, Dr. Blagosklonny co-authored over 30 research articles covering various topics in cancer research, including targeting HSP90, p53, Bcl2, Erb2, and Raf-1.
It was also at that time that, as a sole author, he published several experimental and theoretical papers encompassing the most important themes in his scientific career.
The first key theme focused on the selective protection of normal cells during cancer therapy. Despite the dogma, Dr. Blagosklonny showed that drug resistance provides opportunities for protection of non-resistant normal cells with selective killing of drug-resistant cancer cells. The original concept, titled “Drug-resistance enables selective killing of resistant leukemia cells: exploiting of drug resistance instead of reversal,” was published in Leukemia in 1999. The idea was so unconventional that, at first, it was incorrectly cited as “reversal of resistance” instead of “exploiting of resistance.”
The renowned, world famous scientist Dr. Arthur Pardee was so impressed by Dr. Blagosklonny’s idea that he visited the NCI to meet Mikhail, and in 2001 they co-authored the paper “Exploiting cancer cell cycling for selective protection of normal cells.” Later, when Misha launched Oncotarget, Dr. Pardee became one of the journal’s first Founding Editors.
Dr. Blagosklonny continued to develop the concept of normal cells protection in the following years. These are the most essential publications on this topic:
- 1999: Drug-resistance enables selective killing of resistant leukemia cells: exploiting of drug resistance instead of reversal
- 2001: Exploiting cancer cell cycling for selective protection of normal cells
- 2002: Cyclotherapy: protection of normal cells and unshielding of cancer cells
- 2003: Tissue-selective therapy of cancer
- 2004: Gefitinib (iressa) in oncogene-addictive cancers and therapy for common cancers
- 2005: Why therapeutic response may not prolong the life of a cancer patient: selection for oncogenic resistance
- 2008: “Targeting the absence” and therapeutic engineering for cancer therapy
- 2011: Exploring long-term protection of normal human fibroblasts and epithelial cells from chemotherapy in cell culture
- 2023: Selective protection of normal cells from chemotherapy, while killing drug-resistant cancer cells
The second key theme was Dr. Blagosklonny’s innovative research method to generate new knowledge and ideas by synthesizing facts and observations from seemingly unrelated fields. This concept was published in Nature in 2002, titled “Conceptual biology: Unearthing the gems.”
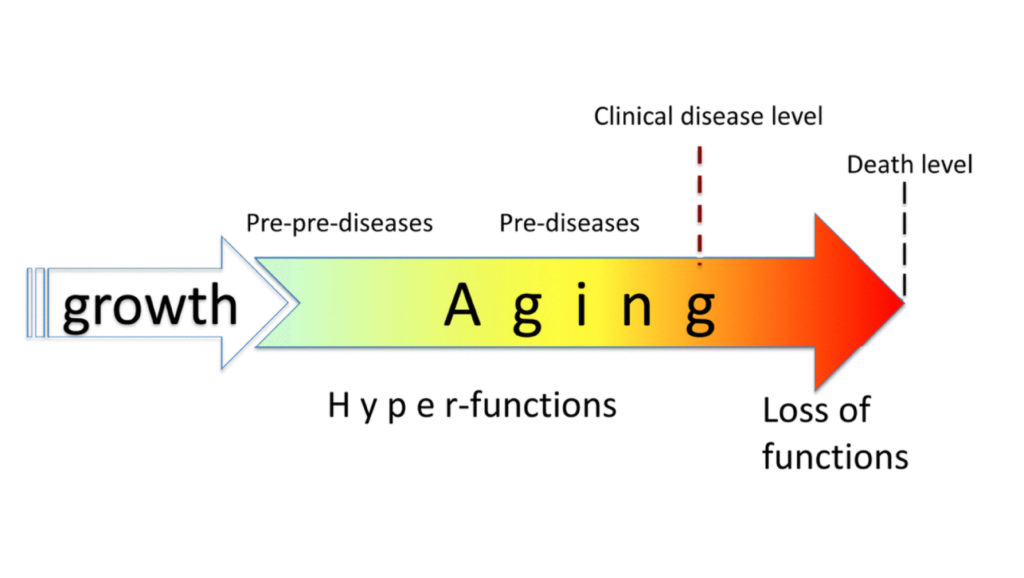
The most significant outcome of this concept was the development of the hyperfunction (or quasi-programmed) theory of aging and the discovery of rapamycin as a potential anti-aging drug. Dr. Blagosklonny first published this idea in 2006, titled “Aging and immortality: quasi-programmed senescence and its pharmacologic inhibition.” Dr. Michael Hall, who discovered the protein TOR (Target of Rapamycin), credited Dr. Blagosklonny for “connecting dots that others don’t even see” in a Scientific American publication.
Dr. Blagosklonny held several faculty positions before joining Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center as Professor of Oncology in 2009, and most recently served there as an adjunct faculty member. In his later years, Dr. Blagosklonny continued to develop his hyperfunction theory of aging and published extensively on the prevention of cellular senescence by rapamycin and other mTOR inhibitors, on cancer (an age-related disease) prevention by slowing down organismal aging, and on combinations of potential anti-aging drugs for use in humans.
These are just a few essential publications on those topics from more than 200 papers:
- 2006: Aging and immortality: quasi-programmed senescence and its pharmacologic inhibition
- 2007: Paradoxes of aging
- 2009: TOR-driven aging: speeding car without brakes
- 2009: Aging-suppressants: cellular senescence (hyperactivation) and its pharmacologic deceleration
- 2009: Growth and aging: a common molecular mechanism
- 2010: Rapamycin and quasi-programmed aging: four years later
- 2010: Increasing healthy lifespan by suppressing aging in our lifetime: preliminary proposal
- 2010: Calorie restriction: decelerating mTOR-driven aging from cells to organisms (including humans)
- 2010: Rapamycin extends maximal lifespan in cancer-prone mice
- 2012: Answering the ultimate question “what is the proximal cause of aging?”
- 2012: Prospective treatment of age-related diseases by slowing down aging
- 2013: Rapamycin extends life- and health span because it slows aging
- 2013: MTOR-driven quasi-programmed aging as a disposable soma theory: blind watchmaker vs. intelligent designer
- 2013: Aging is not programmed: genetic pseudo-program is a shadow of developmental growth
- 2014: Weekly administration of rapamycin improves survival and biomarkers in obese male mice on high-fat diet
- 2014: Geroconversion: irreversible step to cellular senescence
- 2018: Rapamycin, proliferation and geroconversion to senescence
- 2021: DNA- and telomere-damage does not limit lifespan: evidence from rapamycin
- 2021: The hyperfunction theory of aging: three common misconceptions
- 2022: Cell senescence, rapamycin and hyperfunction theory of aging
- 2022: Rapamycin treatment early in life reprograms aging: hyperfunction theory and clinical practice
- 2023: Towards disease-oriented dosing of rapamycin for longevity: does aging exist or only age-related diseases?
- 2023: Are menopause, aging and prostate cancer diseases?
Dr. Blagosklonny has published more than 290 papers in peer-reviewed journals, serving as the first, last, or sole author on nearly all of his papers.
Dr. Blagosklonny was also a very passionate editor. He always dreamed of being an editor. It all began in 2002 when he was invited to become an Editor-in-Chief of the journal Cell Cycle, a position he held for more than 16 years.
Understanding the importance of sharing scientific information without borders, he formulated the idea to launch journals for scientists, by scientists. Since cancer and aging research were always the main focus of his scientific interests, Dr. Blagosklonny, in collaboration with his colleagues, founded Aging in 2009 (co-editors-in-chief: the late Judith Campisi and David Sinclair) and Oncotarget in 2010 (co-editor-in-chief: Andrei Gudkov). Both journals are renowned for their outstanding Editorial Boards, innovative approaches, and significant popularity within the scientific community.
In 2012, Dr. Blagosklonny founded Oncoscience, a unique journal that publishes free of charge for both authors and readers. It can be considered a philanthropic endeavor.
In addition, Dr. Blagosklonny has served as an associate editor or a member of the editorial board of such journals as Cancer Research, International Journal of Cancer, Leukemia, Cell Death Differentiation, Cancer Biology & Therapy, American Journal of Pathology, Autophagy, and others.
Misha was a funny and witty person, who always had very interesting and unconventional opinions about various topics and was always looking for the roots of different matters. Everyone who knew him for a long time felt that they grew as a person because of his influence. He realized himself in this life as a scientist, editor, family man and a friend.
Dr. Blagosklonny envisioned his cancer battle as a mission to explore how metastatic cancer can be treated with curative intent. He published several articles about his battle, sharing original ideas and pushing the boundaries of cancer treatment in collaboration with his doctors. In his own words, Dr. Blagosklonny was near-curing of incurable cancer. He was in remission about two years and stayed active until the last days.
- My battle with cancer. Part 1
- Targeted cancer therapy: the initial high concentration may slow down the selection for resistance
- From osimertinib to preemptive combinations
- Selective protection of normal cells from chemotherapy, while killing drug-resistant cancer cells
- Cancer prevention with rapamycin
- Towards disease-oriented dosing of rapamycin for longevity: does aging exist or only age-related diseases?
Dr. Blagosklonny passed away at his home in Boston, MA.
A special thank you to his colleagues and friends, who continuously supported Misha during his cancer battle: Dr. Tito Fojo, Dr. Wafik El-Deiry, Dr. Andrei Gudkov, Dr. Vadim Gladyshev and Dennis Mangan, to name a few.
He will be deeply missed.
–The entire staff of Impact Journals, LLC